NEW DELHI: Consumption inequality, both in rural and urban areas, has declined in 2023-24 from the previous year for almost all the 18 major states, the detailed results of the Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) showed on Thursday.
Earlier a fact sheet released on HCES by the statistics office last month had shown that the Gini coefficient, a statistical measure of inequality in the population, had declined to 0.24 in 2023-24 from 0.27 in 2022-23 for rural areas and to 0.28 in 2023-24 from 0.31 in 2022-23 for urban areas.
The data also showed that there has been an increase in average monthly per capita consumption expenditure (MPCE) for all the 18 major states in rural and urban areas in 2023-24. The maximum increase in average MPCE in the rural areas was recorded in Odisha (about 14 % from 2022-23), while in urban areas, the maximum increase was witnessed in Punjab (around 13% from 2022-23). The least increase in average MPCE was in Maharashtra (about 3%) and Karnataka (about 5%) in rural and urban areas.
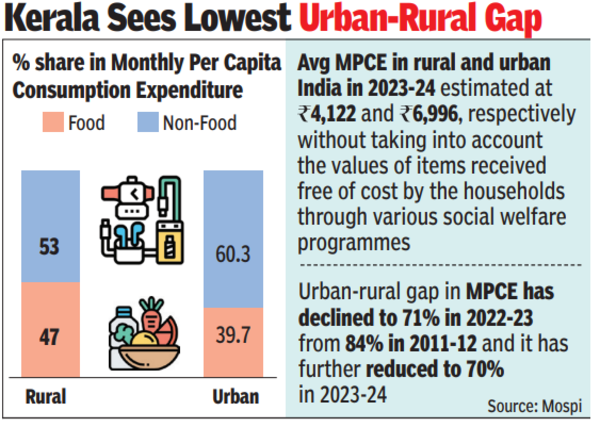
A wide variation in urban-rural difference in average was seen across the 18 major states in 2022-23 and 2023-24. There has been a decline in urban-rural gap in 11 states in 2023-24 compared to the previous year. The lowest urban-rural gap in 2023-24 was seen in Kerala (about 18%) and highest in Jharkhand (around 83%), the survey results showed.
The data showed that food accounted for about 47% of value of the average rural Indian households’ consumption in 2023-24. Among food items, the contribution of beverages, refreshments and processed food has been the highest (9.8%) followed by milk and milk products (8.4%) and vegetables (6%) in rural India.
The share of food in total consumption expenditure of rural households varies from 40.3% (in Kerala) to 53.2% (in Assam). For urban sector, the share of food in consumption expenditure varies from 36.1% (in Maharashtra) to 48.8% (in Bihar).
Share of cereals in total expenditure in rural India varies from 2.6% (in Punjab) to 7.9% (in Jharkhand). In urban India, the share varies from 2.8% (in Haryana) to 5.8% (in Jharkhand).
Contribution of cereals and cereal substitutes in the expenditure was about 5%. Among non-food items, the conveyance (7.59%) was the highest followed by medical (6.83%), clothing, bedding and footwear (6.63%) and durable goods (6.48%).
